Knee Pain: Causes, Symptoms, Treatments, and Prevention Tips
Knee pain is one of the most common complaints in orthopedic care, affecting people of all ages—from athletes recovering from injuries to older adults experiencing arthritis. Knee issues can significantly impact mobility, lifestyle, and overall quality of life.
Understanding the causes of knee pain, recognizing early symptoms, and knowing the appropriate treatments are essential for maintaining joint health and preventing long-term complications. In this comprehensive guide, Dr. Lokesh Dabral, a leading orthopedic surgeon in Dehradun, explains everything you need to know about knee pain, treatment options, and preventive strategies.
Understanding the Knee Joint
The knee is one of the largest and most intricate joints in the body, responsible for bending, rotation, and weight-bearing functions. Its structure includes:
- Bones: Femur (thigh bone), tibia (shin bone), and patella (kneecap)
- Cartilage: Articular cartilage and meniscus cushion the bones and absorb shock
- Ligaments: ACL, PCL, MCL, and LCL provide stability
- Tendons: Connect muscles to bones, enabling movement
- Synovial fluid: Lubricates the joint to reduce friction
Because of its complexity and constant use, the knee is prone to injuries, degenerative conditions, and overuse problems.
Common Causes of Knee Pain
Knee pain can result from injuries, degenerative conditions, or medical disorders. Some of the most common causes include:
1. Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is the most common cause of chronic knee pain in adults over 50. It occurs when the protective cartilage of the knee wears down, leading to stiffness, swelling, and discomfort. Patients often experience worsening pain during physical activity or in the morning.
2. Ligament Injuries
Ligament injuries, particularly Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) tears, frequently occur in athletes or physically active individuals. These injuries often result from sudden twists, impacts, or falls, causing instability, swelling, and difficulty walking.
3. Meniscus Tears
The meniscus acts as a cushion in the knee joint. Meniscus tears can occur due to sports injuries, trauma, or age-related degeneration. Symptoms include pain, swelling, locking, or limited motion of the knee.
4. Tendonitis and Bursitis
Repetitive strain or overuse can inflame tendons (tendonitis) or bursae (bursitis) around the knee. Pain typically worsens during activity and may improve with rest.
5. Fractures or Trauma
Direct impacts from accidents, falls, or sports can fracture bones or dislocate the knee. Prompt orthopedic care is crucial to ensure proper healing and avoid complications.
6. Other Medical Conditions
Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, gout, or infections may also cause knee pain. These require specialized care to prevent long-term damage.
Recognizing Knee Pain Symptoms
Early recognition of symptoms can help prevent worsening conditions. Common signs include:
- Persistent or sharp pain in the knee
- Swelling, redness, or warmth around the joint
- Stiffness, especially after prolonged rest
- Popping or crunching sounds during movement
- Instability or a feeling that the knee may “give way”
- Limited range of motion
If these symptoms persist, consulting an orthopedic specialist is essential.
Diagnosis of Knee Pain
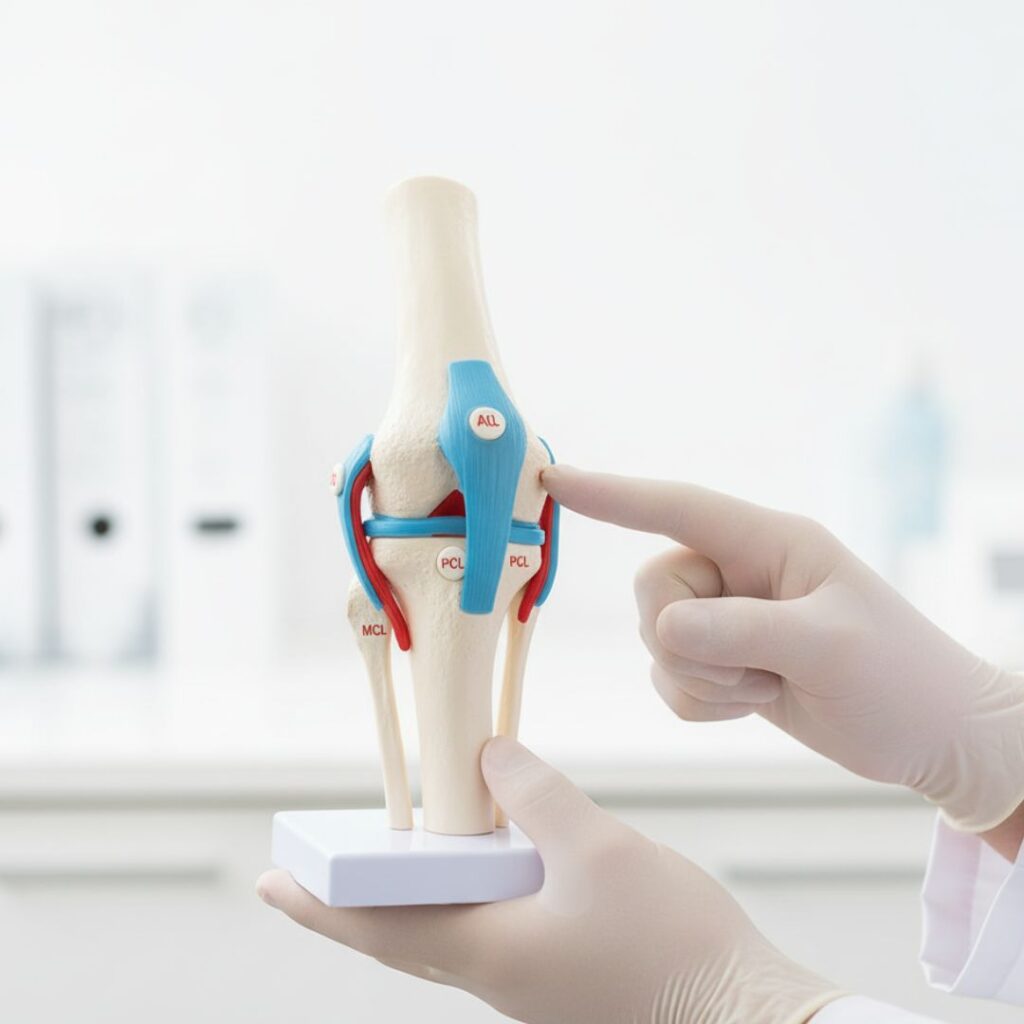
A proper diagnosis typically involves:
- Medical History: Assessment of symptoms, lifestyle, previous injuries, and family history
- Physical Examination: Checking stability, tenderness, swelling, and range of motion
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRI, or CT scans to evaluate bones, cartilage, ligaments, and meniscus
- Laboratory Tests: Blood tests in cases of arthritis or infections
Accurate diagnosis ensures the most effective treatment plan.
Treatment Options for Knee Pain

Treatment depends on the severity and cause of the pain. Dr. Lokesh Dabral provides a comprehensive approach combining non-surgical and surgical options.
1. Non-Surgical Treatments
Many cases can be managed conservatively:
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to strengthen muscles around the knee and improve flexibility
- Medications: Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs
- Lifestyle Modifications: Weight management, low-impact exercise, and avoiding high-stress activities
- Braces and Supports: To stabilize the knee during movement
- Injections: Corticosteroid or hyaluronic acid injections reduce inflammation and improve lubrication
These methods are effective for mild to moderate knee pain and often prevent the need for surgery.
2. Surgical Treatments
If conservative treatments fail, surgical interventions may be necessary:
Arthroscopy
A minimally invasive procedure used to repair meniscus tears, remove loose cartilage, or treat ligament injuries. Smaller incisions result in reduced pain and faster recovery.
Partial Knee Replacement
Replaces only the damaged portion of the knee, preserving healthy tissue and allowing quicker rehabilitation.
Total Knee Replacement
For advanced osteoarthritis or joint damage, total knee replacement replaces the entire knee joint with a prosthetic. Modern techniques minimize pain and improve mobility.
Ligament Reconstruction
ACL and other ligament injuries may require reconstruction using grafts to restore stability. Surgery is often combined with rehabilitation programs for optimal recovery.
Tips for Preventing Knee Pain
Preventive care reduces the risk of knee injuries and degenerative conditions:
- Exercise Regularly: Strengthen quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf muscles
- Maintain Healthy Weight: Reduces stress on knee joints
- Wear Proper Footwear: Supports joint alignment and reduces impact
- Practice Safe Sports Techniques: Use warm-ups, protective gear, and proper form
- Avoid Overuse: Take breaks during repetitive activities
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Include calcium, vitamin D, and protein to support bone and joint health
Regular check-ups with an orthopedic specialist can also help detect issues early and prevent severe complications.
When to Consult an Orthopedic Specialist

Consult a specialist if:
- Pain persists beyond a few weeks
- Swelling or redness does not improve
- Instability, locking, or giving way of the knee occurs
- Pain interferes with daily activities or sleep
Early intervention ensures effective treatment and better long-term outcomes.
Conclusion

Knee pain can affect mobility, independence, and overall quality of life. Understanding its causes, recognizing symptoms, and exploring appropriate treatments—ranging from non-surgical methods to advanced surgical interventions—can significantly improve joint health.
Dr. Lokesh Dabral, a leading orthopedic surgeon in Dehradun, provides expert diagnosis, modern treatments, and patient-centered care for all types of knee problems. With proper treatment, rehabilitation, and preventive measures, individuals can maintain healthy knees and enjoy an active, pain-free lifestyle.
