Hip Pain: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment Options, and Prevention Tips
The hip joint plays a vital role in supporting body weight, enabling movement, and maintaining balance. When hip pain develops, even simple tasks like walking, climbing stairs, or sitting for long hours can become uncomfortable.
Dr. Lokesh Dabral, one of the leading orthopedic surgeons in Dehradun, explains that hip pain can stem from several causes — from injuries and age-related wear to lifestyle factors and medical conditions. Understanding its causes, recognizing early warning signs, and seeking timely treatment can prevent complications and help restore mobility.
Understanding the Hip Joint
Hip pain can arise from a variety of sources. The most frequent include:
1. Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is one of the most common causes of chronic hip pain. It occurs when cartilage — the protective tissue cushioning the bones — wears down over time, leading to stiffness, inflammation, and pain during movement. Patients often report pain that worsens in the morning or after long activity periods.
2. Rheumatoid Arthritis
An autoimmune disorder that causes inflammation in the hip joint, resulting in pain, swelling, and reduced mobility. Unlike osteoarthritis, it can affect both hips simultaneously.
3. Hip Fractures
A fracture usually occurs in older adults due to falls or in younger individuals after severe trauma. It requires immediate medical attention to avoid complications such as immobility or avascular necrosis (loss of blood supply to bone tissue).
4. Bursitis
The bursae are small sacs filled with fluid that cushion the hip joint. Overuse or prolonged pressure can cause inflammation, known as bursitis, which results in tenderness and sharp pain during movement.
5. Tendonitis
Repetitive activities, improper posture, or sports injuries can strain hip tendons, causing inflammation and localized pain.
6. Labral Tear
The labrum is a ring of cartilage surrounding the hip socket that ensures smooth movement. Tears in the labrum often cause clicking, stiffness, and pain during rotation or exercise.
7. Sciatica and Referred Pain
Sometimes, pain that feels like a hip problem originates from the lower back or spine, radiating down to the hip or thigh.
Symptoms of Hip Pain
The location and intensity of hip pain depend on the underlying cause. Common symptoms include:
- Sharp or dull ache in the groin, thigh, or outer hip
- Stiffness and reduced range of motion
- Pain that worsens with movement or prolonged sitting
- Swelling or warmth around the joint
- Clicking, locking, or grinding sensations
- Difficulty walking, standing, or balancing
Persistent pain lasting more than a few days should never be ignored. Early diagnosis can prevent deterioration and promote faster healing.
Diagnosing Hip Pain
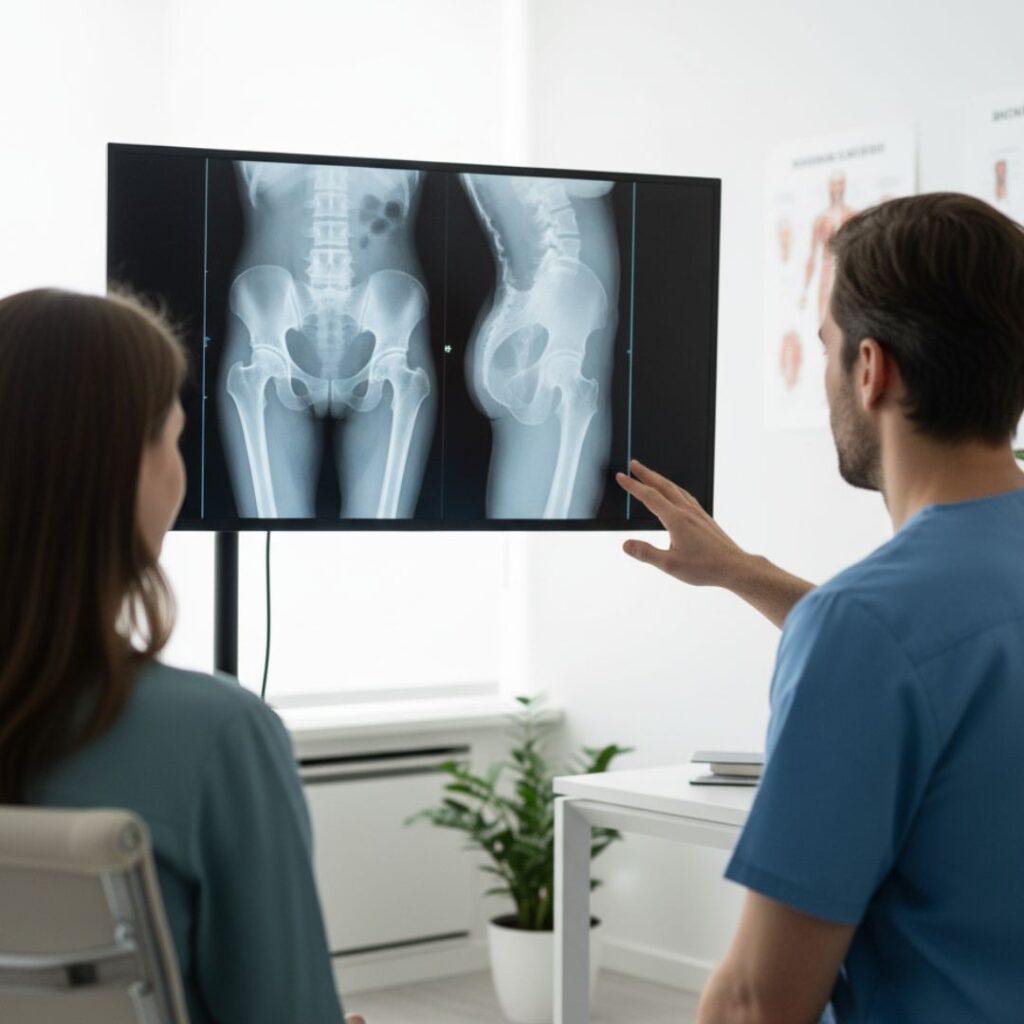
Dr. Lokesh Dabral follows a detailed diagnostic approach to identify the root cause of hip discomfort. This includes:
- Physical Examination: Checking range of motion, tenderness, and gait
- Medical History: Assessing injuries, activity level, and health conditions
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRI, or CT scans to evaluate bones, cartilage, and soft tissue
- Blood Tests: Detecting signs of infection, inflammation, or autoimmune disease
Accurate diagnosis allows the doctor to design the most effective and individualized treatment plan.
Treatment Options for Hip Pain
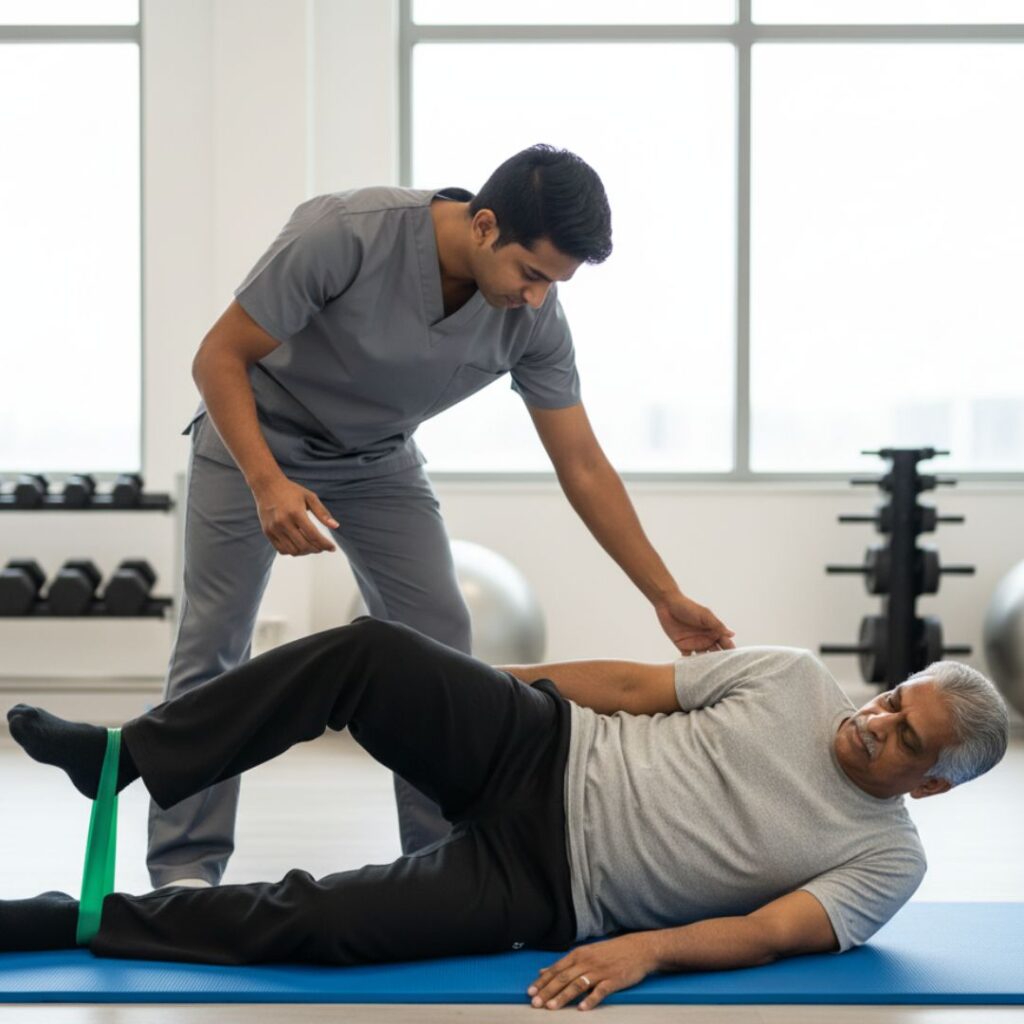

Treatment depends on the severity, cause, and patient’s lifestyle needs. Most cases respond well to non-surgical approaches, while severe conditions may require surgical intervention.
1. Non-Surgical Treatments

1. Physical Therapy
Targeted exercises strengthen the hip muscles, improve flexibility, and reduce stiffness. Regular physiotherapy enhances stability and helps prevent future injuries.
2. Medications
Anti-inflammatory drugs and pain relievers minimize discomfort and swelling. In some cases, short-term muscle relaxants or corticosteroids may be prescribed.
3.Lifestyle Modifications
Maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding prolonged sitting, and switching to low-impact activities such as swimming or cycling help protect the hip joint.
4.Injections
Corticosteroid or platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections can reduce inflammation and support tissue healing in chronic conditions.
5.Assistive Devices
Using walking sticks or orthotic supports can relieve pressure on the affected joint and improve mobility.
2. Surgical Treatments
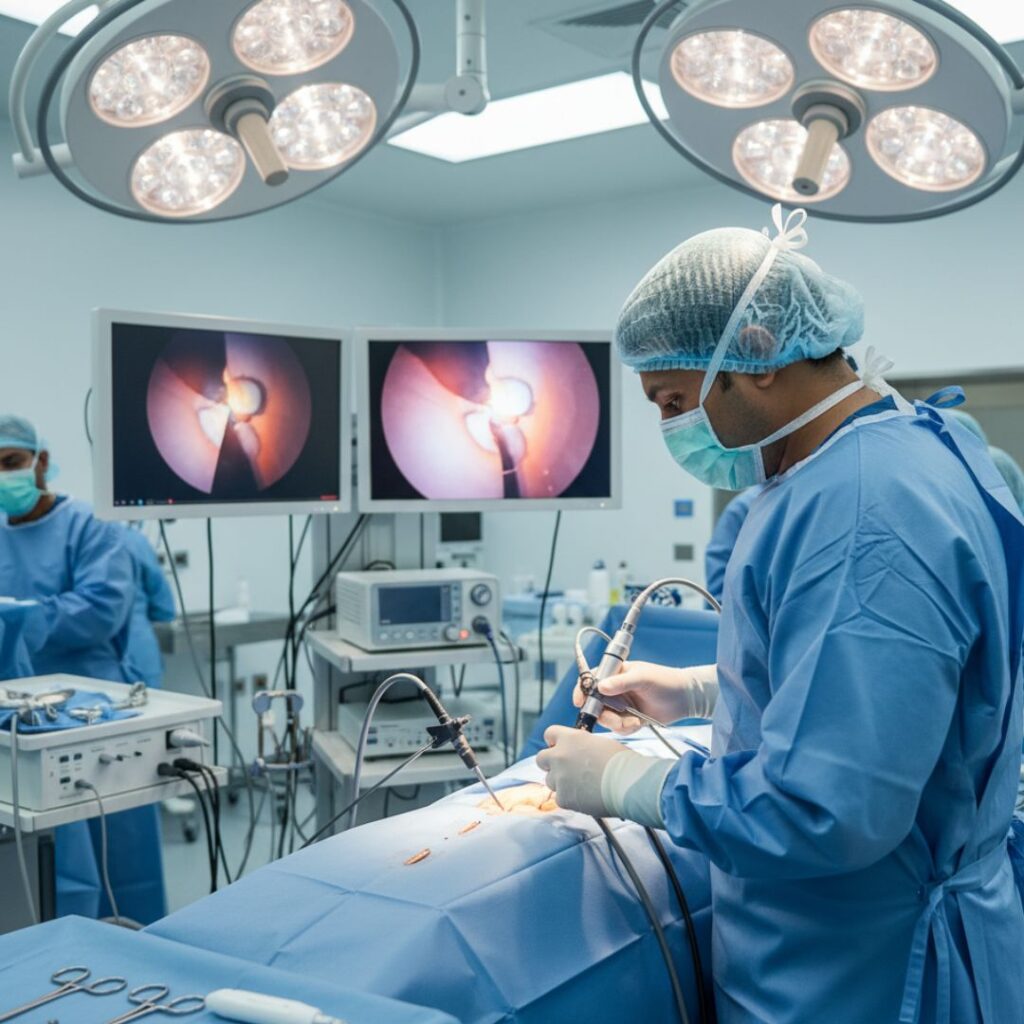
When conservative treatments fail, surgery may be the best option to restore function and relieve pain.
1. Hip Arthroscopy
A minimally invasive procedure used to repair labral tears, remove loose cartilage, or treat impingement. It involves small incisions and offers faster recovery times.
2. Partial Hip Replacement
Recommended when only part of the hip joint is damaged, this procedure replaces the affected section with a prosthetic implant.
3. Total Hip Replacement
In advanced arthritis or severe trauma, a total hip replacement replaces both the femoral head and the socket with artificial components. This modern technique offers excellent long-term outcomes, pain relief, and improved quality of life
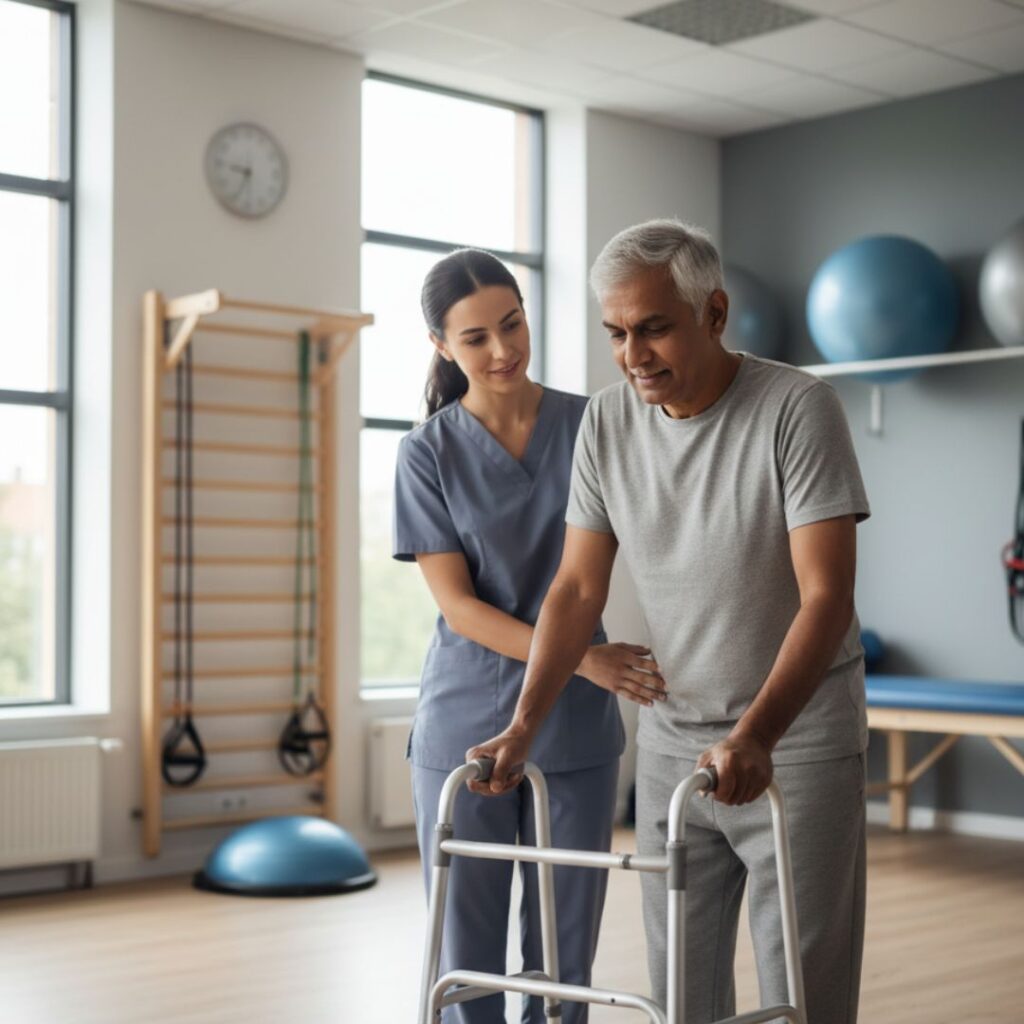
Recovery and Rehabilitation

After treatment or surgery, recovery focuses on regaining strength, stability, and mobility. A customized rehabilitation program may include:
- Gradual physiotherapy sessions
- Range-of-motion and strengthening exercises
- Proper rest and gradual activity resumption
- Weight management and posture correction
- Routine follow-up appointments with the orthopedic specialist
Adhering to a guided recovery plan ensures faster healing and reduces the risk of re-injury.
Prevention Tips for Healthy Hips

Preventing hip pain is easier than treating it. Here are practical tips to maintain strong and pain-free hips:
- Stay Physically Active: Regular exercise keeps joints flexible and muscles strong.
- Maintain Ideal Weight: Excess weight increases pressure on hip joints.
- Use Correct Posture: Sit and stand with good alignment to avoid stress.
- Avoid Sudden Movements: Warm up before workouts or sports.
- Strengthen Core Muscles: A strong core supports hip stability.
- Choose Supportive Footwear: Reduces stress on lower joints.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Include calcium, vitamin D, and omega-3 fatty acids for joint health.
Simple lifestyle adjustments can significantly reduce hip discomfort and delay degenerative changes.
When to Consult an Orthopedic Surgeon
You should see an orthopedic specialist if you experience:
- Constant pain that lasts more than a week
- Difficulty walking or bearing weight
- Swelling, redness, or deformity near the hip
- Pain disrupting daily routines or sleep
- Previous injuries with recurring pain
Early consultation helps identify the problem before it worsens. Timely medical care can often prevent surgery and ensure faster recovery.
